Treatments
>
Musculo-Skeletal
Treatments for Musculo-Skeletal Conditions
Click on any of the items below to jump down the page to the relevant section.
We have included a lot of information about how you can benefit from Acupuncture Treatments and how they work.
Back Pain:
The back is the structure that supports most of our daily activities. Over time and through repetitive use we develop postures that render the back muscles less capable of adapting to stresses as they need to be. Muscular strain occurs and is the most common form of back discomfort, which is usually tolerable early on. These patterns become ingrained in us and if left unattended become more problematic in later years. The muscular system of the back is intended to be a balanced entity. When this balance is altered stresses are unable to be absorbed and distributed producing pain patterns.
Acupuncture acts to release the areas where muscles are too tight and support or tone those that are weakened by dis-use. The result is a more balanced back with the ability to support us in our daily activities.


Sports Injuries:
The most common sports injuries are sprains and strains. Acupuncture’s anti-inflammatory effects often benefit acutely injured muscles, tendons, or ligaments. All patients, and particularly athletes and physically active individuals, may benefit from acupuncture’s muscle-cueing, motor pattern influences to address the faulty body mechanics that predispose one to injury. In truth, many so-called “over-use” injuries are really “improper-use” injuries that require retraining movements and skills to avoid mechanically stressing structural weak spots. Acupuncture can facilitate this retraining. Acupuncture also plays a role in retraining the body after injury, to restore proper movement patterns.
Chronic Pain:
Pain that is unrelenting has many causes. The repetitiveness of a pain signal can become a cause in and of itself. In the treatment of a chronic pain pattern acupuncture addresses both the underlying cause of the pain as well as the pain signal.

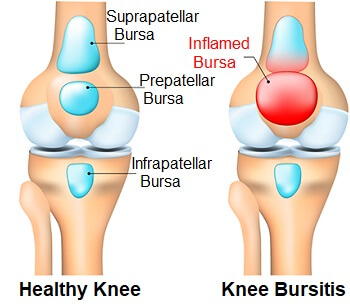
Bursitis:
A bursa is a soft tissue sac filled with fluid that your body uses to reduce friction between moveable structural components. Often bursae will exist between tendons or between tendons and bone.
Bursitis is the inflammation of the sac that surrounds our major joints. These sacs are fluid filled and lubricate the joint space where loaded movement occurs. Irritation of the local structures is thought to be the cause. There are some opinions that weather changes affect this structure. Acupuncture and related techniques are often very effective in reducing this inflammation which relieves much of the pain. Other strategies in reducing inflammation are sometimes required and can be combined with acupuncture therapy, for more effective and lasting results.
Joint Pain:
Studies on the effects of acupuncture on joint pain have been limited, and results vary between individuals. Often other treatments to decrease inflammation along with acupuncture help more completely than acupuncture alone. These articles describe research results:
Arthritis.org article
WebMD article

